What is revenue forecasting?
Revenue forecasting estimates future earnings from selling products or services over a set period (weekly, monthly, quarterly, annually). It relies on the current state of the business, previous performance, and external factors to make educated assumptions. This comprehensive approach evaluates the business as a whole, not just focusing on sales or marketing efforts.
Key considerations in revenue forecasting include the competitive landscape, production and staffing capacity, and broader economic trends. Accurate forecasts are crucial for establishing a company’s budget and are combined with expense and investment estimates to create profit and cash flow projections. These projections significantly influence decisions on advertising spend, hiring, and other strategic actions.
Effective revenue forecasting, grounded in historical trends, market conditions, and business strategy, impacts investments, spending, investor perceptions, and talent attraction. Analysts leverage company performance data, competitive and economic factors, and financial modeling techniques to create these forecasts, ensuring that businesses can make informed, decisions.
Why is revenue forecasting important?
Revenue forecasting is a cornerstone in shaping a company’s future outlook and guiding essential business decisions. It influences both short-term and long-term goals, helping prepare the organization for the future. A well-structured forecast is pivotal for budgeting various aspects such as new hires, marketing campaigns, facilities, equipment, and research and development (R&D).
Finance teams utilize revenue forecasts to estimate profit and cash flow by incorporating these projections into the cost elements outlined in the income statement. For example, a forecast predicting a 5% revenue growth might necessitate an 8% increase in advertising expenditure and a 5% boost in the sales team.
Moreover, higher revenue can lead to better economies of scale, effectively reducing the cost of goods sold. It is crucial to assess whether the finance staff can manage increased sales levels and ensure there is sufficient working capital to support this growth.
Revenue forecasts have a significant impact on publicly traded companies. Wall Street analysts rely on these forecasts to make informed investment decisions, and missing revenue projections can result in stock downgrades. For private companies, accurate revenue forecasts are vital for attracting investment or preparing the business for sale.
In essence, a revenue forecast serves as a key indicator of a business’s strength and investment potential, playing a crucial role in its overall financial health and strategic planning.
Best Practices for Revenue Forecasting
Accurately forecasting revenue involves a deep understanding of your business’s current status, historical data, and external influences. A systematic approach is essential for making informed decisions and crafting strategies that drive business success.
Compiling Comprehensive Financial Data
First, compile comprehensive financial data by collecting detailed financial information, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Using financial software, and your CRM can automate data collection, track transactions, and categorize expenses.
Determining the Forecasting Time Frame
Next, determine the forecasting time frame by creating both annual and quarterly revenue forecasts. Focus on shorter time frames for greater accuracy, acknowledging the inherent uncertainty in long-term predictions.
Evaluating Internal Business Factors
Evaluate internal business factors by analyzing current product and service offerings, including plans for new launches or expansions. Assess internal capabilities, such as production capacity, staffing, and logistics. Consider strategic plans, including marketing campaigns, mergers, and acquisitions.
Incorporating External Influences
Incorporate external influences by identifying and assessing external factors like market demand, seasonality, regulatory changes, and broader economic conditions. Integrate these external elements to provide a more comprehensive view in your forecast.
Identifying Constraints and Risks
Identify constraints and risks by examining sensitivity to changes, assessing the impact of shifts in consumer behavior or business investment on your forecast, and identifying potential supply chain issues such as material shortages, labor constraints, or logistical challenges. Model different risk scenarios to understand the impact of various risks on your forecast.
Utilizing Forecasting Tools and Software
Utilize forecasting tools and software to streamline the process. Choose appropriate financial forecasting software to automate data analysis, consolidate information, and access prebuilt forecasting models. Select suitable forecasting techniques that align with your business model, such as time-series analysis or regression analysis, and tailor these methods to fit specific needs, whether accounting for seasonality or consistent growth.
You can also expand on tools you’re already using. Incorporating tools to forecast revenue directly inside of your CRM gives you the most up-to-date data and the most reliable revenue forecasts without the need for manual spreadsheets.
Continuously Monitoring and Adjusting
Continuously monitor and adjust by setting up real-time dashboards to track forecast accuracy and budget variances. Regularly update your forecast based on actual performance and changing external conditions to ensure forecasts remain relevant and actionable.
By following these steps and leveraging the right tools, you can develop accurate revenue forecasts that inform strategic decisions and support business growth.
Revenue Forecasting Models
Straight Line Forecasting
Straight-line forecasting uses past data to estimate future company growth, assuming a constant and predictable rate of increase. This method is best suited for well-established industries with stable market conditions.
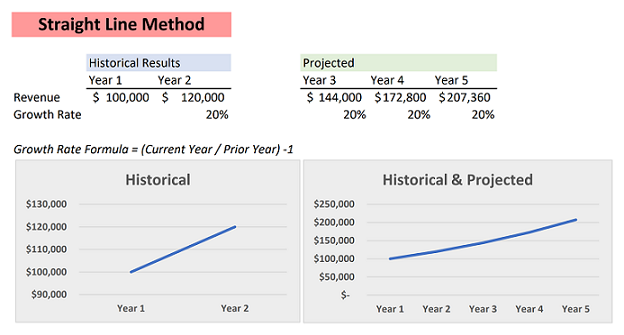
Source: Insights For Professionals
Moving Average Forecasting
This approach leverages historical data to examine shorter time periods, uncovering market trends and seasonal variations. It is particularly useful for businesses experiencing seasonal changes, offering a more detailed view of short-term revenue patterns.
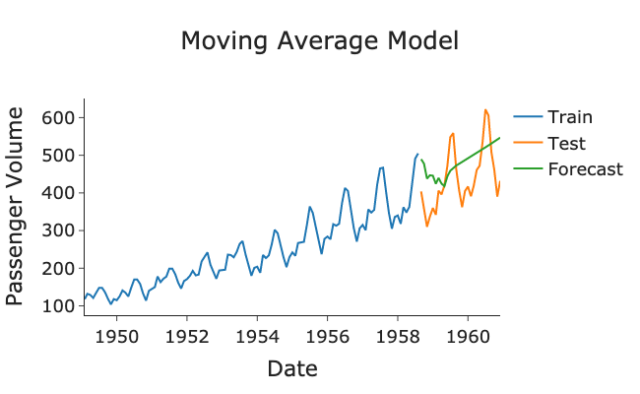
Source: Towards Data Science
Time Series Forecasting
Time series forecasting examines particular time periods, such as months, quarters, or years, to predict future revenue. This method is beneficial for businesses with cyclical revenue patterns, aiding in the planning of campaigns and the effective allocation of resources.
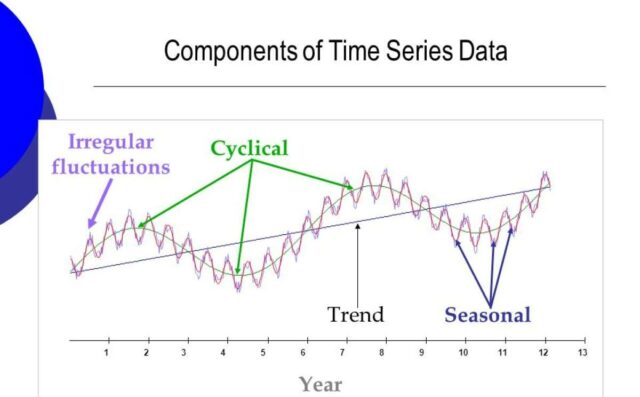
Source: Springboard
Weighted moving average forecast.
This time series technique employs a weighted average of past data points to forecast the next value in the sequence. It is especially useful for tracking monthly revenue outcomes and refining short-term forecasts. For instance, you might analyze your revenues from January through April to estimate May’s revenue.
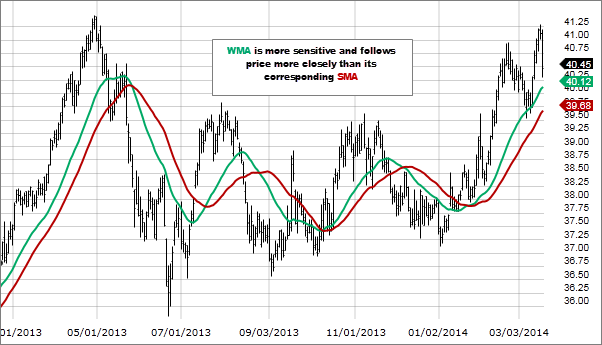
Source: Fidelity
Why you shouldn’t forecast revenue in spreadsheets
Using spreadsheets for revenue forecasting is a widespread practice, but it comes with several challenges. Here are some significant issues:
Lag Time Associated with Manual Forecasting in Spreadsheets
Manually collecting and consolidating data for forecasting is slow and delays decision-making as forecasts are often based on outdated information. Inefficient workflows and bottlenecks further impede the timely availability of updated forecasts, impacting business responsiveness.
Manual Data Entry Errors: Forecasting revenue often requires extensive manual data entry, increasing the risk of mistakes. These errors can compromise the accuracy of forecasts and lead to financial mismanagement.
Version Control Issues: When multiple users update the same spreadsheet, it becomes difficult to track changes and identify who made specific edits. This lack of clarity can result in errors and inaccuracies in the data.
Collaboration Limitations: Spreadsheets are not ideal for real-time collaboration. Typically, team members must share files via email, leading to delays in decision-making and potential miscommunication.
Performance Issues with Large Data Sets: Spreadsheets can struggle to handle large volumes of data, becoming slow, unresponsive, or even crashing. This makes it challenging to conduct in-depth data analysis.
Additionally, spreadsheets do not provide a comprehensive view of sales and emerging trends. Users often need to consolidate information from various sources to gain a complete understanding.
Salesforce offers a robust platform designed to provide a single source of truth. It enables real-time collaboration, reducing errors through automated data entry and efficient handling of large data sets. However, it has limitations in its native forecasting tools.
Salesforce may not fully capture the complexity of diverse revenue streams, leading to less accurate forecasts, especially for businesses with intricate sales cycles multiple product lines, or consumption pricing models. The need for manual data manipulation for advanced forecasting can still introduce errors and delays, despite the platform’s automated features.
revVana + Salesforce: The Best way to forecast revenue
revVana brings finance logic and different revenue models directly into Salesforce, eliminating the need for spreadsheets for forecasting. This integration allows for real-time, accurate revenue forecasting within a familiar platform. revVana also enables consumption forecasting, allowing businesses to predict revenue based on customer usage patterns and other consumption metrics.
If you’re ready to enhance your revenue forecasting capabilities and drive business growth, contact us to learn how revVana can support your efforts. Our tools and expertise can help you implement the best revenue forecasting models tailored to your business needs.